New top story from Time: Pediatric COVID-19 Cases Are Surging, Pushing Hospitals—and Health Care Workers—to Their Breaking Points
Aug. 20 was a good day in the pediatric intensive care unit at Children’s Hospital New Orleans. Carvase Perrilloux, a two-month-old baby who’d come in about a week earlier with respiratory syncytial virus and COVID-19, was finally ready to breathe without the ventilator keeping his tiny body alive. “You did it!” nurses in PPE cooed as they removed the tube from his airway and he took his first solo gasp, bare toes kicking.
Downstairs, Quintetta Edwards was preparing for her 17-year-old son, Nelson Alexis III, to be discharged after spending more than two weeks in the hospital with COVID-19—first in the ICU, then stabilizing on an acute-care floor. “Fortunately, he never regressed,” Edwards says from outside Nelson’s room, the door marked with signs warning of potential COVID-19 exposure inside. “He’s progressing, slowly but surely.”
[time-brightcove not-tgx=”true”]
The nurses and doctors who care for the sickest patients at Children’s Hospital New Orleans (CHNO) have to take the good where they can these days. On Aug. 6, Louisiana Governor John Bel Edwards announced that more than 3,000 children statewide had been diagnosed with COVID-19 over the course of just four days. That same week, about a quarter of Louisiana children tested for COVID-19 by the state’s largest health system turned out to have the virus.
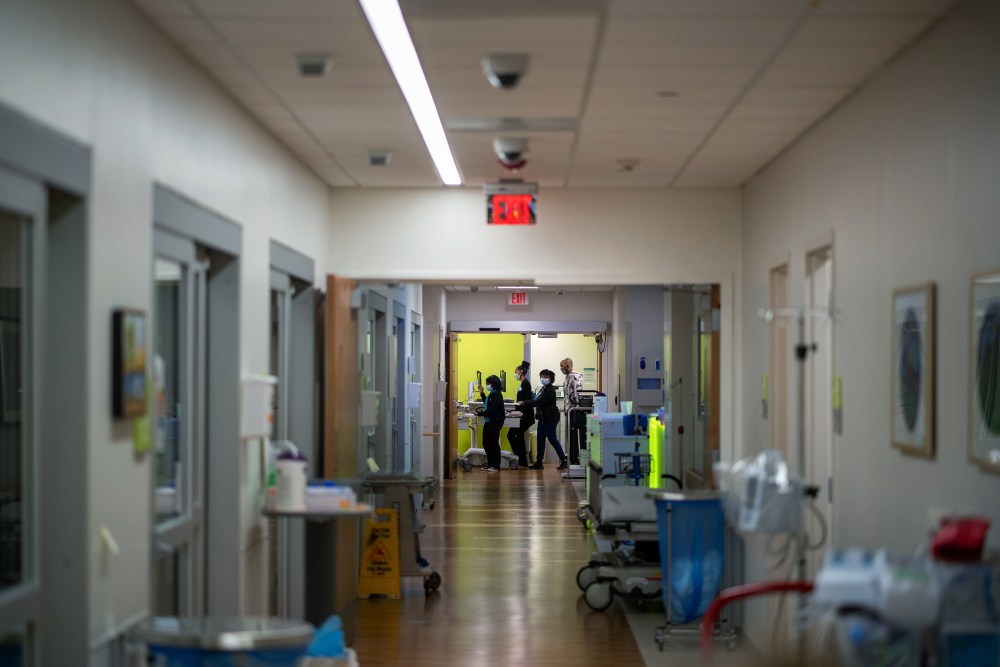

Seventy young patients ended up in treatment at CHNO during the 30 days ending Aug. 23. Prior to this summer, the hospital had never had to care for more than seven COVID-19 patients at a time, and usually fewer than that; on any given day in August, that number has been at least in the mid-teens, enough that the facility had to call in a medical strike team from Rhode Island to help manage the surge.
CHNO isn’t alone. The extra-transmissible Delta variant has ushered in a new chapter of the pandemic. For the first time, pediatric hospitals are struggling to treat the number of young patients developing severe cases of COVID-19. A record high of more than 1,900 children were hospitalized nationwide on Aug. 14—and unlike during previous spikes, infections have so far been clustered largely in states with low vaccine coverage, meaning hospitals in undervaccinated states like Louisiana, Florida, Tennessee, Alabama and Texas are drowning. “Our hospital system across Alabama is beyond capacity. Last week we had net negative ICU beds, and that’s pediatric and adult together,” says Dr. David Kimberlin, co-director of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s of Alabama. “Doctors are doing CPR in the back of pickup trucks.”
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/ZumvZ/2/
This grim scenario may seem shocking, given one of the pandemic’s long-standing silver linings: that children, for the most part, are spared from the worst of COVID-19. About 400 children nationwide have died from COVID-19 since the pandemic began, and most pediatric hospitals have seen no more than a handful of patients at a time—which makes the current surge in the South and parts of the Midwest especially unnerving.
There is no evidence that the Delta variant is causing more severe disease than previous strains, says Dr. Sean O’Leary, vice chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) committee on infectious diseases. Less than 2% of children who have caught COVID-19 during this wave landed in the hospital—roughly the same percentage as during earlier phases of the pandemic, according to a TIME analysis of AAP and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services data. An even smaller percentage of children die from the disease, though some have gone on to develop complications like the inflammatory condition MIS-C.
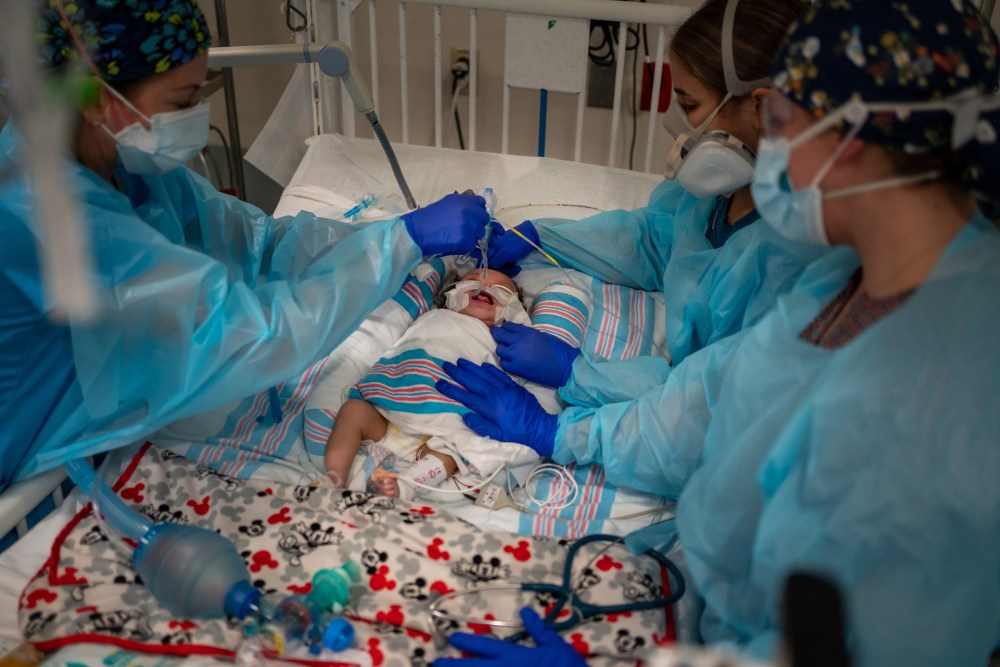
The difference seems to be that the highly contagious Delta strain is tearing through all demographic groups at a furious clip, currently contributing to the more than 140,000 infections reported in the U.S. on any given day. It’s a depressing numbers game: If 100 children become infected, one or two might end up in the hospital. Push the caseload up to 180,000—the number of kids diagnosed with the virus nationwide during the week ending Aug. 19—and at least 1,800 are likely to get sick enough to need hospitalization.
Children have also drawn a short straw. Viruses are wily, seeking out and infecting vulnerable hosts at all costs. Without authorized vaccines for people younger than 12, any child who has not previously been infected has no immunity against SARS-CoV-2, meaning the virus effectively has free rein among America’s 50 million youngest residents. Even among older children who can get vaccinated, rates are low: just 35% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 45% of 16- and 17-year-olds are fully vaccinated, according to U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
While each individual child has a low chance of developing severe disease, the current pediatric surge, which has been compounded by an off-season spike in RSV and parainfluenza cases, has grave implications for health care networks. Even before the pandemic, health care access was a struggle in parts of the South and Midwest. In Arkansas, for example, there is only one pediatric hospital system to serve the state’s more than 3 million residents. A rural hospital could have fewer than 10 ICU beds, meaning even a small coronavirus surge could push it beyond its limits. “Down here in the deep South, we are getting slammed to the point where, honestly, our health systems may collapse,” Kimberlin says. “What that means is, if you have a stroke, you die at home.”
There’s a reason pediatric ICUs are dangerously full in Tennessee and Texas but, at least at the moment, not Maryland and Massachusetts. In each of the latter two states, more than 60% of residents are fully vaccinated; in the former, about 41% and 46%, respectively. States with high vaccination rates also tend to be more aggressive about other precautions, like indoor mask mandates.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/n60o2/3/
There are exceptions—pediatric hospitalizations are ticking up in California (151 admissions this week vs. 68 a month ago) and New York (46 vs. 20 a month ago), two states with high vaccine coverage—and no one can predict what the virus will do in the future. But it stands to reason that more kids are getting sick in states like Louisiana, where only about 40% of the population is fully vaccinated and more than 4,600 new diagnoses are being reported among its 4.6 million residents each day. “Kids don’t tend to drive what’s going on; they tend to reflect what’s going on in the surrounding community,” O’Leary says.
That children are largely at the mercy of the adults in their communities is one of the cruelest quirks of this surge. “It’s hard, because you don’t want to be judgmental” of people who haven’t gotten the shot, says Dr. Michael Blancaneaux, an emergency medicine physician at CHNO.
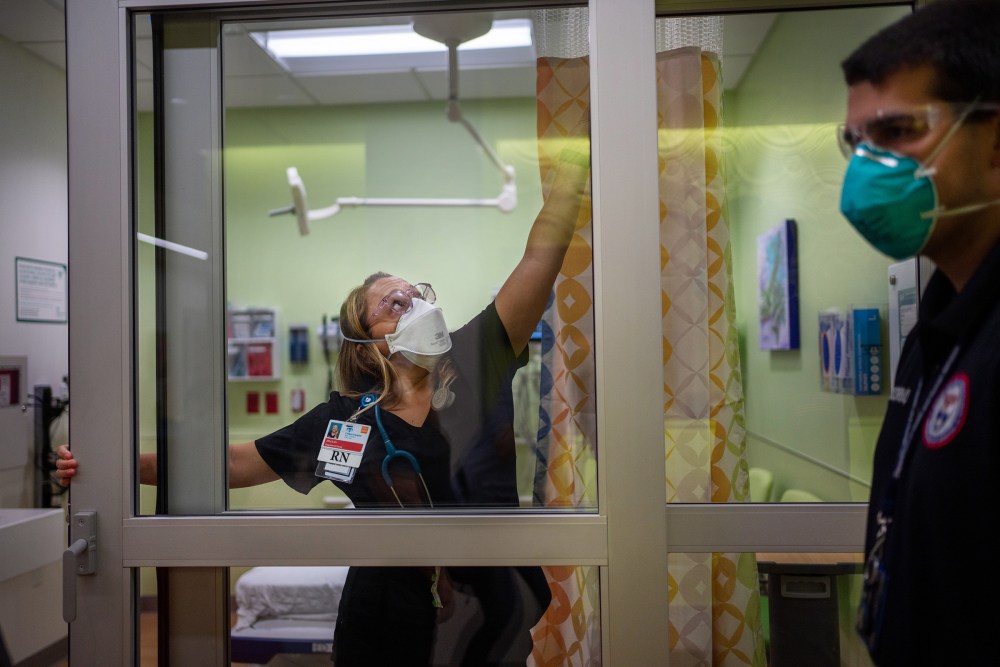

But it’s also clear, he says, that the decisions of unvaccinated adults are endangering the lives of children who couldn’t be vaccinated even if they wanted to be. While many CHNO staff members are careful to say vaccination is a personal choice, there’s a discernible subtext beneath their politeness: they wish more people in the community would choose to vaccinate themselves and their families. For the doctors who treat young patients—and who are exhausted from worrying about COVID-19 for, as Blancaneaux says, what feels like forever—learning that their families are unvaccinated, or failing to take other precautions, is a bitter pill to swallow, and one that makes it difficult to keep going about their essential work unfazed. Indeed, a sign hanging in CHNO’s emergency-department bathroom directs staff to “wipe away tears” before returning to work.
“How do you try to tell someone why they should care about the life of a child?” Alabama’s Kimberlin asks. “I don’t know.”
Paul Decerbo has been a member of the Rhode Island-1 Disaster Medical Assistance Team for more than 10 years, long enough to become the squad’s commander. Three months out of each year, when there’s an emergency anywhere in the U.S., Decerbo knows he may have to prepare himself and a team of on-call medics, nurses and doctors to ship out to the scene of the crisis for two weeks. Sometimes, that’s the site of a natural disaster. For the last 18 months, it’s mostly been wherever COVID-19 cases are surging and local hospitals are at their breaking points.
Decerbo deployed six times last year. But when he got a call from CHNO this summer, asking for people who could help treat emergency-department patients, he faced a new challenge. He’d need an entire team of people ready to treat COVID-19 patients and trained in pediatrics—something not required during prior coronavirus surges, when the vast majority of patients were adults. Ultimately, he had to look beyond Rhode Island and assemble a squad of health-care workers from multiple states to meet that need.
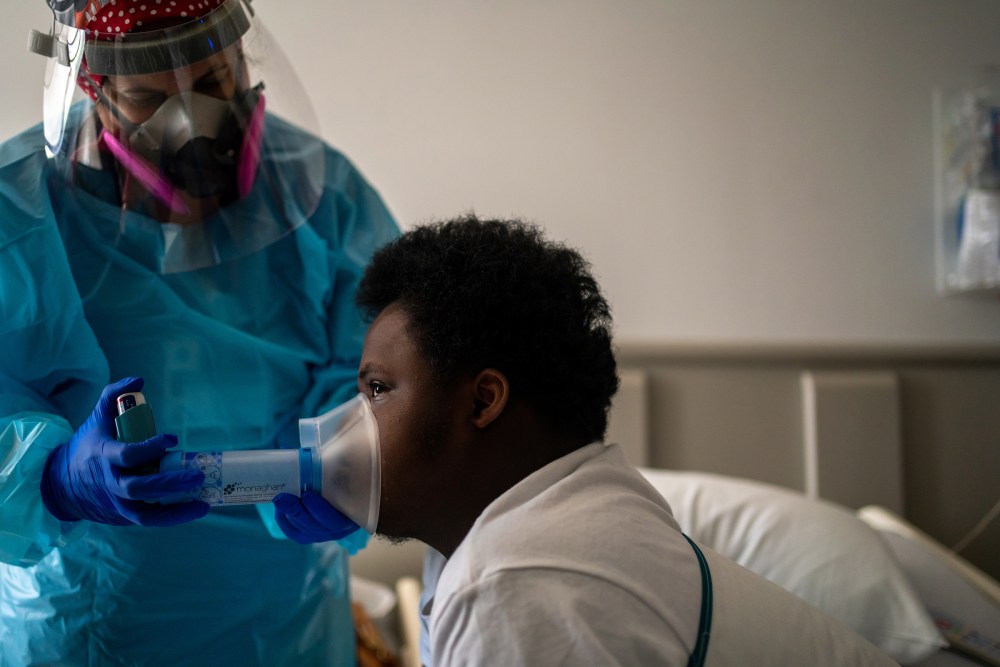
CHNO’s resident staffers weren’t quite prepared for the uptick in pediatric cases, either. “It was a shock,” Blancaneaux says. After a year of few-and-far-between cases in the pediatric hospital, “All of a sudden, eight out of the 20 patients I saw [in a day] were COVID positive.” It’s gotten to the point, he says, where doctors assume any patient who comes in with flu-like symptoms has COVID-19.
The hospital’s quiet atmosphere hides the work happening behind the scenes to keep pace with that increase. CHNO has implemented an incentive program to encourage current staff nurses to pick up extra shifts, and has hired about 150 new nurses to help manage the patient load.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/eSb5K/3/
Perhaps more concerning, the current spike began in July, before most schools in Louisiana had started back up. As the school year continues, Delta will almost undoubtedly find new footholds. No one wants to consider what happens if this is the ascent of a bell curve, rather than the peak—particularly since vaccines for the youngest Americans may not be available until late 2021 or early 2022.
Even once the shots are authorized, children too young to consent to treatment will be reliant on their parents’ willingness to get them vaccinated. That’s a troubling prospect since, in a recent Kaiser Family Foundation survey, only 26% of parents with kids ages 5 to 11, and 20% of those with kids younger than 5, said they would vaccinate their children right away.

In some cases, that may be because parents still do not believe young children need to be vaccinated, considering their low odds of dying or becoming hospitalized. But there are always exceptions to rules, and they’re showing up every day in pediatric ICUs. Jordan Ohlsen, a nurse who works on CHNO’s acute-care floor, says some parents don’t realize how serious the virus can be until their child is the one in a hospital bed. “Once the child does get sick, their [parents’] conception of what the virus is [changes],” Ohlsen says. “When they come in and see their kid sick, in their brain it switches to, ‘This is something I should be worried about,’ or ‘I should have gotten them vaccinated.’”
If there is any optimism buried within the current pediatric surge, it’s that perhaps some parents will have that realization before their child gets sick, rather than after. But with vaccine authorization for young children at least a few months away, the immediate battle is in convincing adults to get their shots, thereby hopefully driving down the total amount of virus circulating in each community. Delta seems to be scaring at least some holdouts into action. On average, more than 700,000 people in the U.S. are now getting a COVID-19 vaccine each day, a higher number than the country has reported since June. But there’s a long way to go, and not a lot of time to travel it.
Particularly in areas where infection rates are high, health officials must encourage people to go back to basics, the AAP’s O’Leary says. New Orleans, for its part, has reimplemented mask mandates and now requires proof of vaccination or a negative test from anyone who wants to visit an indoor bar, restaurant or music venue, lending a somewhat subdued air to many parts of the usually buoyant city.
“Use the mitigation measures we know work,” O’Leary says. “Wear masks when you’re around other people, particularly in enclosed spaces….Avoid places where lots of people are congregating.”
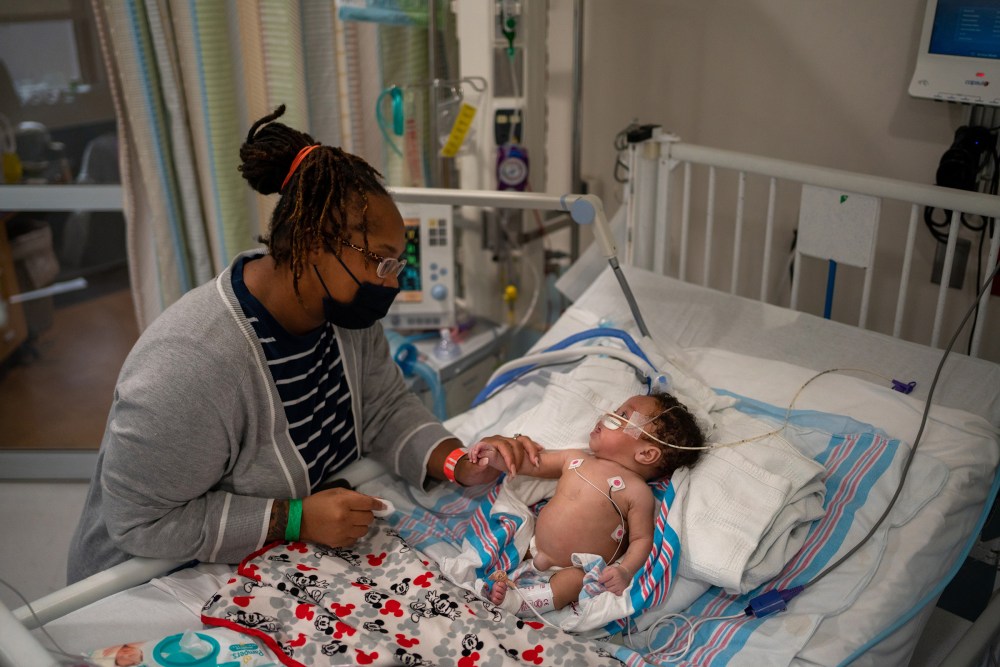
Unless and until health officials can convince a tired and disillusioned populace to return to precautions they wanted to leave in the past, COVID-19 will keep spreading. A small number of patients, no matter how young, will land in the hospital. And day after day, health care workers will don their gas-mask-like respirators, gowns and goggles to care for them, many worrying all the while about bringing COVID-19 home to their own children.
The staff at CHNO makes a valiant effort to stay positive and keep smiling beneath their masks—a trait, perhaps, of choosing to work in pediatrics. But Blancaneaux admits it can be difficult this far into a pandemic, when the tools for ending it are in nearly every drugstore in the country. “Everyone is frustrated and worn out and upset,” he says. “You feel unsupported by the public because we keep fighting against it. And a large part of it is preventable.”
—With reporting by Emily Barone
Comments
Post a Comment